Osmotic Pressure Calculator
The process of osmosis is one that is integral to life and how organisms work. Use this tool to calculate the osmotic pressure required to stop the process of osmosis from occurring.
Required Information
Osmotic Pressure:
Create Date: October 16, 2024
Last Modified Date: January 14, 2025
To calculate the osmotic pressure required to halt the process of osmosis, the following variables are required:
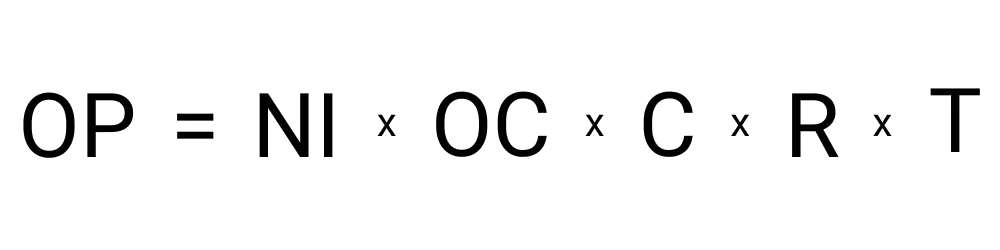
Your result will be an amount of pressure. For example, you may get an answer of 1,846 bars. That means there must be 1,846 bars of pressure for the process of osmosis to freeze up and halt in your specific scenario. The unit of pressure measurement can be changed between the most common ones, not just bars.
Our osmotic pressure tool is designed to be efficient and simple. The steps involved with using our tool include:
Imagine a lab technician working in a research laboratory dealing with plant cells. They need to find out how much pressure is required to prevent water from moving into the cells, which are suspended in a particular solution. This information is crucial for understanding how external solutions can affect plant cell behavior and stability.
Osmotic pressure is the minimum pressure needed to prevent the flow of a solvent, like water, through a semipermeable membrane into a solution of higher solute concentration.
Osmosis is the process of solvent movement across a semipermeable membrane, while osmotic pressure is the amount of pressure needed to stop that movement.
The osmotic pressure of the human body depends on the temperature. For example, at 37 degrees Celsius, the average osmotic pressure of a person's blood is approximately 7.8 bar.
According to Britannica online, osmotic pressure can be used to preserve food. High concentrations of salts or sugars in foods create a hypertonic environment, which dehydrates microorganisms and helps preserve foods like pickles or jams for extended periods.