Create Date: July 12, 2024
Last Modified Date: January 15, 2025
Calculating price elasticity can be done with the following variables:
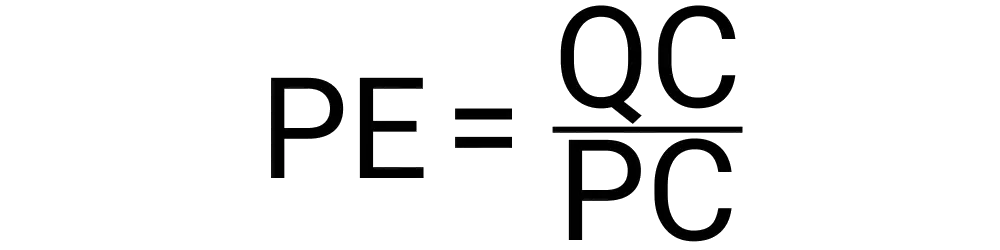
Your result will be a single number that will likely not be a whole number. If the number you get is below 1.0, that means it is inelastic. This means that the change in price results in a less than proportional change in quantity demanded. If your result is over 1.0 that means it is elastic. This means that a greater than 1% change in price results in a more than proportional change in quantity demanded. Alternatively, if the result is exactly 1.0, it means a 1% change in price results in a proportional 1% change in quantity demanded.
Calculating the price elasticity of demand can be time-consuming and confusing. Our tool makes it easier than ever to calculate this metric with little to no work involved. The steps involved with using the tool includes:
We are going to be placing an order for a new batch of our products. We want to make sure we are getting the best deal and to do that we will review the tiered pricing the proposed to us and find the price elasticity of demand for it. The first tier would be 1,000 units for $7.50 each for a total of $7,500. The other tier would be 1,500 units for $7.30 each for a total of $10,950. We can then use this tool by entering 7,500 into the initial price field, 1,000 into the initial quantity field, $10,950 into the final price field and then 1,500 into the final quantity field. We can now hit calculate to get an answer of 1.09, meaning this is elastic.
Yes, if you get a value that is less than 1 then it is inelastic which means despite the change in price, the change in quantity was also rather small.