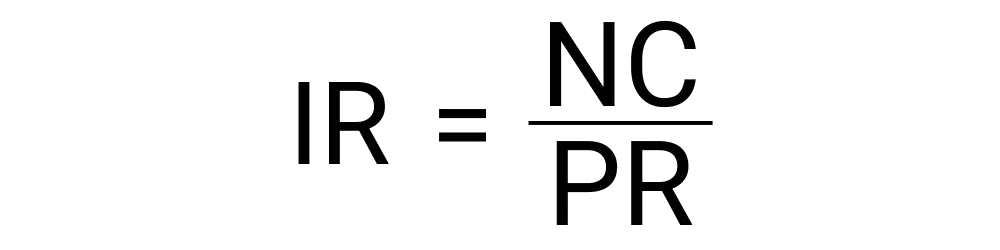The History of Incidence Rate
Incidence rate is a more modern term and a concept that is rather new compared to being old. Its roots do not go back thousands of years. While ancient civilizations may have detected patterns with diseases spreading, the thought of a metric like incident rate was never talked about until much later in history.
Arguably the first major step in taking diseases and tracking their spread very seriously came with the bubonic plague in 1347. With massive numbers being affected, deaths would be tracked and counted as best as they could, this is the first real step towards caring about this type of information.
Another major step was when John Snow, a British physician, tracked the spread of Cholera in London. He would map out the cases and calculate the number of new infections per population, making it an early version of incidence rate.
With science continuing to advance, the early 1900s would introduce the category of epidemiology. Soon after, the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) would standardize disease tracking worldwide. By the mid 1900s, the mathematical formula for incidence rate would be introduced and welcomed.
Incidence Rate - Frequently Asked Questions
Simply put, incidence rate describes how quickly disease occurs or spreads in a population. This can be useful for personal safety and for planning mitigation measures to limit spread.
A high incidence rate indicates that the disease or illness is spreading quickly, suggesting a greater likelihood of new individuals contracting the illness within the population.
A low incidence rate means that fewer new cases are being reported relative to the population at risk, suggesting that the spread is under control or not very rapid.
Page Glossary
Understanding incidence rate can be difficult if some of the terms and keywords used are not ones you understand. Here we shed some more light on some of these terms.
| Term |
Definition |
| Cases |
Each time a person is infected with a disease or ailment that is a new case. |
| Epidemiology |
The study of infectious diseases. |